Asteroid 1999 JV6 passed by the Earth at a distance of about 12 460 000
km (32.42 times the average distance between the Earth and the
Moon, or 8.3% of the average distance between the Sun and the Earth),
slightly after 11.15 am GMT on Moday 5 January 2015. There was no
danger of the asteroid hitting us, though were it to do so it would have
presented a serious threat. 1999 JV6 has an estimated
equivalent diameter of 190-590 m (i.e. it is estimated that a spherical
object with the same volume would be 190-590 m in diameter), and an
object of this size would be predicted to be capable of passing through
the Earth's atmosphere relatively intact, impacting the ground with an
energy equivalent to about 200-10 000 megatons of TNT (roughly 11 800-588
000
times the energy of the Hiroshima bomb). Such an event
would result in a crater between 2.5 and 8 km across, cause devastation
on a global scale and would have the potential to affect the climate
globally for decades or even centuries after the impact event.
The calculated orbit of 1999 JV6. JPL Small Body Database Browser.
1999 JV6 was discovered on 13 May 1999 by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Lincoln Near Earth Asteroid Research Laboratory
in Socorro, New Mexico. The designation 1999 JV6 implies that it was
the 171st asteroid (asteroid V6) discovered in the first half of May 1999 (period 1999 J).
1999 JV6 has a 369 day year orbital period and an eccentric
orbit tilted at an angle of 5.3° to the plane of the Solar System, which
takes it from 0.69 AU from the Sun (i.e. 69% of the average distance at
which the Earth orbits the Sun, slightly inside the orbit of Venus) to 1.32 AU from the Sun (i.e. 1.32% of
the average distance at which the Earth orbits the Sun). It is
therefore classed as an Apollo Group Asteroid (an asteroid that is on
average further from the Sun than the Earth, but which does get closer).
This means that close encounters between the asteroid and Earth areextremely common, with the
last having occured in January 2014 this year and the next predicted in January 2016 (it will continue to pass us each January until 2022, then not come close to Earth again till May 2077). As an asteroid larger than 150 m in diameter that occasionally comes
within 0.05 AU of the Earth, 1999 JV6 is also classified as a
Potentially Hazardous Asteroid.
See also...
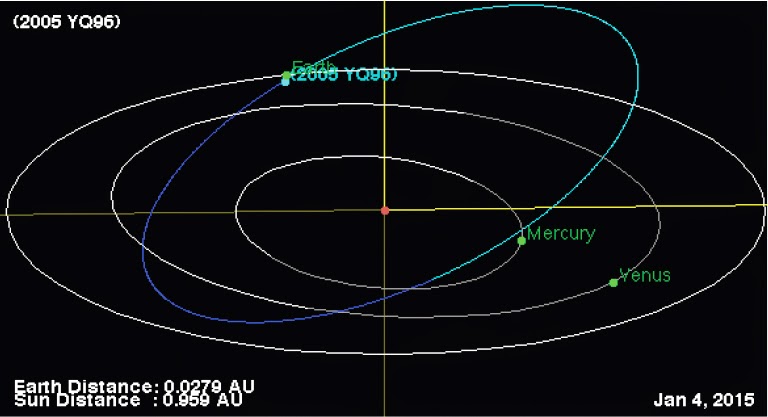 Asteroid 2005 YQ96 passes the Earth. Asteroid 2005 YQ96 passed by the Earth at a distance of about 3 967 000
km (10.32 times the average distance between the Earth and the
Moon, or 2.7% of the average distance between the Sun and the Earth)...
Asteroid 2005 YQ96 passes the Earth. Asteroid 2005 YQ96 passed by the Earth at a distance of about 3 967 000
km (10.32 times the average distance between the Earth and the
Moon, or 2.7% of the average distance between the Sun and the Earth)...
The Quadratid Meteor Shower is one of the brightest meteor showers of
the year, often producing over 100 meteors per hour at its peak, which
falls on the night of 3-4 January each year, and is predicted to peak at
2.00 am GMT on Sunday 4 January 2015. The meteor...
 Asteroid 2001 XY10 passes the Earth. Asteroid 2001 XY10 passed by the Earth at a distance of about 18 540 000
km (48.22 times the average distance between the Earth and the
Moon, or 12% of the average distance between the Sun and the Earth), at...
Asteroid 2001 XY10 passes the Earth. Asteroid 2001 XY10 passed by the Earth at a distance of about 18 540 000
km (48.22 times the average distance between the Earth and the
Moon, or 12% of the average distance between the Sun and the Earth), at...
Follow Sciency Thoughts on Facebook.