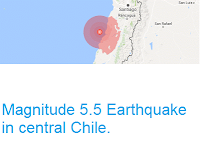
The United States Geological Survey recorded
a Magnitude 5.1 Earthquake at a depth of 75.7 km, 98 km to the southeast of the city of Antofagasta in the Chilean province of the same name,
slightly after 6.10 am local time (slightly after 10.10 am GMT) on
Wednesday 26 July 2017. There are no reports of
any damage or injuries associated with this event, but people have
reported feeling locally.
The approximate location of the 26 July 2017 Antofagasta Earthquake. USGS.
Chile
is located on the west coast of South America, which is also the
convergent margin between the Nazca and South American Plates. The Nazca
Plate is being subducted beneath the South American Plate and is
sinking beneath the South American Plate. This is not a smooth process,
the rocks of the two plates continuously stick together then, as the
pressure builds up, break apart again, causing Earthquakes. As the Nazca
Plate sinks deeper it is partially melted by the heat of the Earth's
interior. Some of the melted material then rises up through the
overlying South American Plate as magma, fuelling the volcanoes of the
Chilean Andes.
The subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate, and how it causes Earthquakes and volcanoes. Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center.
Witness
accounts of Earthquakes can help geologists to understand these events,
and the structures that cause them. The international non-profit
organisation Earthquake Report is interested in hearing from people who may have felt this event; if you felt this quake then you can report it to Earthquake Report here.
Follow Sciency Thoughts on Facebook.