Flights to and from Bali have been halted following an eruption on Mount Agung, a 3000 m stratovolcano (cone shaped volcano made up of layers of ash and lava) on the eastern part of the island, on the evening of Friday 24 May 2019. The event lasted about four-and-a-half minutes, and threw incandescent rocks up to 3 km from the volcano, as well as causing ash falls in nearby communities. Volcanic ash is extremely hazardous to aircraft in a number of ways. At
its most obvious it is opaque, both visually and to radar. Then it is
abrasive, ash particles physically scour aircraft, damaging components
and frosting windows. However the ash is most dangerous when it is
sucked into jet engines, here the high temperatures can melt the tiny
silica particles, forming volcanic glass which then clogs engine. When
this happens the only hope the aircraft has is to dive sharply, in the
hope that cold air passing through the engine during the descent will
cause the glass to shatter, allowing the engine to be restarted.
Obviously this is a procedure that pilots try to avoid having to
perform. Despite this there has been no change to the volcano's alert status,
with the 4 km exclusion zone currently in place around the
volcano thought to be sufficient.
Eruption on Mount Agung, Bali, on 24 May 2019. ABC News.
Mount Agung became active in September 2017, for the first time in
over fifty years. This activity has caused considerable concern on the
island, as when it last erupted in 1963-4, when it produced ash columns
reaching 10 km above its 3 km high
summit and lava flows that reached 7 km from the volcano, as well as
triggering a series of lahars and pyroclastic flows that killed over 200
people, making people on the island very cautious about any future
eruptions.
The approximate location of Mount Agung. Google Maps.
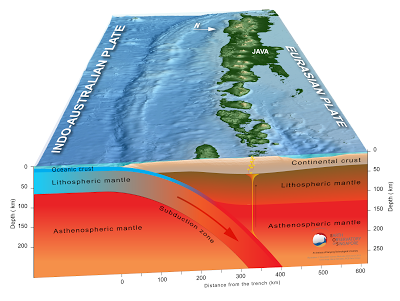
The
Indo-Australian Plate, which underlies the Indian Ocean to the south of
Java, Bali and Lombok, is being subducted beneath the Sunda Plate, a
breakaway part of the Eurasian Plate which underlies the islands and
neighbouring Sumatra, along the Sunda Trench, passing under the islands,
where friction between the two plates can cause Earthquakes. As the
Indo-Australian Plate sinks further into the Earth it is partially
melted and some of the melted material rises through the overlying Sunda
Plate as magma, fuelling the volcanoes of Java and neighbouring
islands.
Subduction along the Sunda Trench beneath Java, Bali and Lombok. Earth Observatory of Singapore.
See also...
Follow Sciency Thoughts on Facebook.