Asteroid 2019 QU3 passed by the Earth at a distance of about 670 000
km (1.74 times the average 0distance between the Earth and the Moon, or
0.45% of the distance between the Earth and the Sun), at about 1.40 pm
GMT on Saturday 24 August 2019. There was no danger of
the asteroid hitting us, though were it to do so it would not have
presented a significant threat. 2019 QU3 has an estimated
equivalent
diameter of 3-11 m (i.e. it is estimated that a spherical object
with
the same volume would be 3-11 m in diameter), and an object of this
size
would be expected to explode in
an airburst (an explosion caused by superheating from friction with the
Earth's atmosphere, which is greater than that caused by simply
falling, due to the orbital momentum of the asteroid) in the atmosphere more than 30 km above the ground, with only fragmentary material
reaching the Earth's surface.
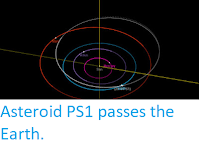
The calculated orbit of 2019 QU3. JPL Small Body Database.
2019 QU3 was discovered on 27 August 2019 (three days after its closest approach to the Earth) by the University of Hawaii's PANSTARRS telescope. The
designation 2019 QU3 implies that it was the 92nd asteroid (asteroid U3 -
in numbering asteroids the letters A-Y, excluding I, are assigned
numbers from 1 to 24, with a number added to the end each time the
alphabet is ended, so that A = 1, A1 = 25, A2 = 49, etc., which means that U3 = 20 + (24 X 3) = 92)
discovered in the second half of August 2019 (period 2019 Q).
2019 QU3 has a 927 day orbital period and an eccentric orbit
tilted at an angle of 0.74° to the plane of the Solar System, which
takes it from 1.01 AU from the Sun (i.e. 101% of he average distance at
which the Earth orbits the Sun) to 2.71 AU from the Sun (i.e. 271% of
the
average distance at which the Earth orbits the Sun, and considerably outside the orbit of the planet Mars). It is therefore
classed as an Amor Group Asteroid (an asteroid which comes close to the
Earth, but which is never closer to the Sun than the Earth is). This means that 2019 QU3 has occasional close encounters with the planet Earth, with the last having occurred in June 2014.
See also...
Follow Sciency Thoughts on Facebook.