Asteroid 2019 GS19 passed by the Earth at a distance of about 743 000
km (1.93 times the average distance between the Earth and the Moon, or
0.50% of the distance between the Earth and the Sun), slightly before 7.35 am
GMT on Thursday 11 April 2019. There was no danger of
the asteroid hitting us, though were it to do so it would not have
presented a significant threat. 2019 GT19 has an estimated
equivalent
diameter of 14-45 m (i.e. it is estimated that a spherical object
with
the same volume would be 14-45 m in diameter), and an object of this
size
would be expected to explode in
an airburst (an explosion caused by superheating from friction with the
Earth's atmosphere, which is greater than that caused by simply
falling, due to the orbital momentum of the asteroid) in the atmosphere
between 20 and 10 km above the ground, with only fragmentary material
reaching the Earth's surface.
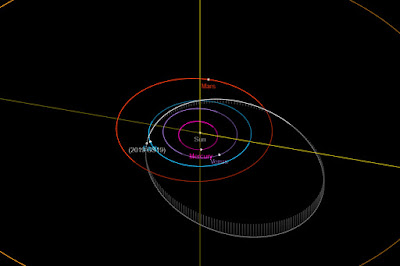
The calculated orbit of 2019 GS19. Minor Planet Center.
2019 GS19 was discovered on 11 April 2019 (the day of its closest approach to the Earth) by the Palomar Transient Factory at Palomar Observatory.
The
designation 2019 GS19 implies that it was the 474th asteroid (asteroid S19 -
in numbering asteroids the letters A-Y, excluding I, are assigned
numbers from 1 to 24, with a number added to the end each time the
alphabet is ended, so that A = 1, A1 = 25, A2 = 49, etc., which means that T19 = 18 + (24 X 19) = 474)
discovered in the first half of April 2019 (period 2019 G).
2019 GS19 is
calculated to have
an 1015 day orbital period and an eccentric orbit
tilted at an angle of 6.59° to the plane of the Solar System, which
takes it from 0.82 AU from the Sun (i.e. 82% of the the average distance
at
which the Earth orbits the Sun) to 3.14 AU from the Sun (i.e. 314% of
the
average distance at which the Earth orbits the Sun, more than twice the
distance at which the planet Mars orbits). It is therefore
classed as an
Apollo Group Asteroid (an asteroid that is on average further from the
Sun than the Earth, but which does get closer). This means that close
encounters between the asteroid and the Earth occur occasionally, with the
last calculated to have happened in April 1924 and the next predicted
for May 2196. The asteroid also has occasional encounters with the planet Mars, with the last thought to have occurred in September 2007.
See also...
Follow Sciency Thoughts on Facebook.